Ethereum Gas Fees Hit Multi-Year Lows After Market Crash, Raising Security Concerns
0
0

Ethereum gas fees have fallen to their lowest level in years. On Sunday, transaction costs plunged to 0.067 Gwei, marking one of the lowest Ethereum gas fees seen in recent years.
The drop coincides with a period of stagnation in the crypto market since an abrupt plunge last month. Activity on the Ethereum network has cooled, data from Etherscan indicates. Falling gas prices spark elation, fear among traders and analysts.
Ethereum Gas Fees Hit Record Lows After Market Crash
Ethereum gas fees are now cheaper than ever. A token swap costs only $0.11. Selling or buying an NFT costs about $0.19. Bridging a digital asset to another network costs $0.04. Borrowing on-chain now costs just $0.09.
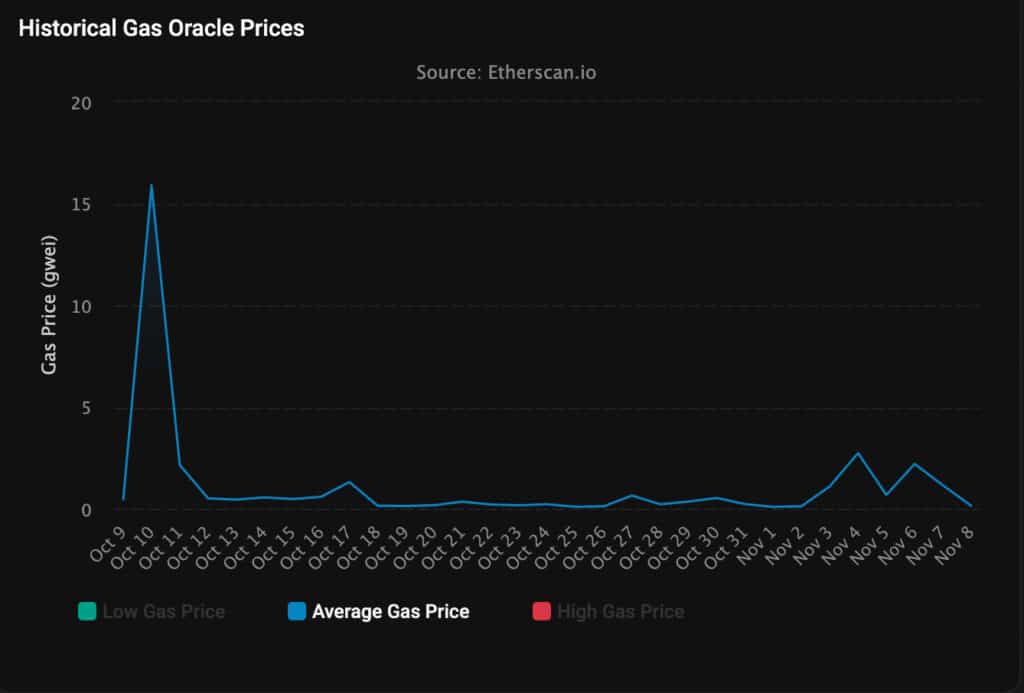
These low numbers mark a big change from early October. At that time, Ethereum gas fees surged to 15.9 Gwei during the flash crash that wiped out many altcoins. Within two days, fees fell below 0.5 Gwei and stayed under 1 Gwei through October and November.
Investors Eye Low-Cost Opportunities
Many traders see a window to make cheaper on-chain transactions. They can swap tokens, mint NFTs, or move assets across blockchains with minimal cost. But experts warn that low Ethereum gas fees might not be a good sign.
Also Read: Ethereum Stablecoin Volume Soars to Record Heights in October
They say fewer people are using the network. This could weaken Ethereum’s economy and reduce validator income. If fees stay low for too long, network security could suffer as validator rewards shrink.
Impact of the Dencun Upgrade
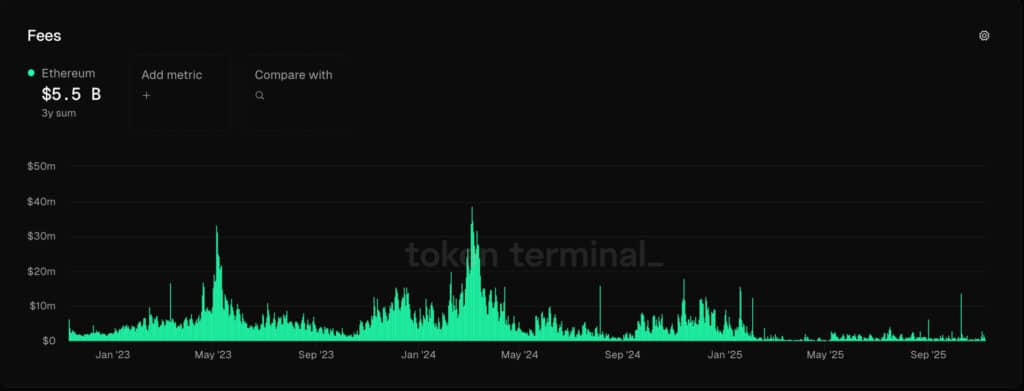
The latest fall in Ethereum gas fees began after the Dencun upgrade in March 2024. The upgrade helped lower costs by moving more transactions to layer-2 scaling networks. But the change had an unexpected effect. Ethereum’s main layer revenue dropped by nearly 99%.
The Layer-2 Paradox
Layer-2 networks like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base are helping Ethereum grow. They let users transact at lower costs and higher speeds. Yet, these same networks are cutting into Ethereum’s layer-1 revenue.
Binance research shows that this creates internal competition. Users who once paid high Ethereum gas fees on the main chain are now moving to cheaper sidechains. While this improves scalability, it reduces profits for the main network.
Economic and Security Concerns
Low Ethereum gas fees bring financial risks. Validators rely on these fees as a key part of their rewards. If revenue keeps falling, it could discourage participation in securing the network.
Analysts warn that fewer active validators could weaken Ethereum’s defense against attacks. They also point out that low fees may mean less user demand. This could suggest that people are shifting to other blockchains that offer faster performance or better incentives.
Wider Market and Economic Context
Ethereum gas fees are dropping at a time when global markets are uncertain. In the US, recently, President Trump proposed a $2000 dividend paid for by revenue from tariffs.
Analysts think this could drive some short-term spending and lift crypto prices. But others fear it could lead to inflation and drive down the value of the dollar. That, in turn, might send investors fleeing back toward cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum.
Future Outlook for Ethereum Gas Fees
Experts are divided over what comes next. Others speculate that gas fees on Ethereum will increase again after market activities level out. Others believe that the network’s scaling model will keep fees low indefinitely.
The months ahead will reveal whether Ethereum can manage to be at once affordable and sustainable. If fees remain that low, it could usher in a new era for the network — one that’s good for users but tests its economics.
Conclusion
The drastic decrease in Ethereum gas fees is a reminder of how delicate the balance between growth and security can be. Low-cost transactions allow more people around the world to use Ethereum.
But if fees remain low, validators might lose their incentive to secure the network. Now Ethereum must figure out how to keep both costs low and rewards strong in order to remain competitive in the changing world of blockchain.
Also Read: Ethereum Price Forecast: Analysts Predict ETH to Reach $4,500 by Year-End?
Appendix: Glossary of Key Terms
Ethereum Gas Fees: The tiny payments users issue to process and finalize transactions on the Ethereum blockchain.
Gwei: A tiny increment of Ether, used to price Ethereum gas fees. One Gwei is equivalent to one billionth of an Ether.
Layer-1 Blockchain: The root Ethereum network where all core transactions, smart contracts, and on-chain interactions occur.
Layer-2: Another system, layered on top of Ethereum, that allows faster and cheaper transactions to occur in a way that takes pressure off the main network.
Dencun Upgrade: A big Ethereum upgrade that occurred in 2024, which lowered gas prices and allowed for more scalability by shifting usage to layer-2 networks.
Validators: Actors that validate transactions and maintain the Ethereum blockchain network; they are rewarded for doing so, including a percentage of gas fees.
Frequently Asked Questions Ethereum Gas Fees
1. What are Ethereum gas fees?
They are small payments users make to process and confirm transactions on the Ethereum blockchain.
2. Why have Ethereum gas fees dropped?
They fell due to lower network activity and the use of layer-2 scaling networks after the Dencun upgrade.
3. Are low fees good for Ethereum?
They make the network cheaper to use but can reduce validator income and weaken security.
4. Will Ethereum gas fees rise again?
Yes, they could increase if market activity or congestion grows during a new crypto rally.
Read More: Ethereum Gas Fees Hit Multi-Year Lows After Market Crash, Raising Security Concerns">Ethereum Gas Fees Hit Multi-Year Lows After Market Crash, Raising Security Concerns
0
0
 Manage all your crypto, NFT and DeFi from one place
Manage all your crypto, NFT and DeFi from one placeSecurely connect the portfolio you’re using to start.






