Bitcoin Staking: What It Means and How It Works Today
1
0

Bitcoin was designed as a secure, conservative monetary network rather than a yield-generating system. Its proof-of-work consensus prioritizes immutability and censorship resistance, keeping it as pristine as possible.
Yet over the past few years, “Bitcoin staking” has emerged as a common term in institutional and crypto-native discussions. In practice, this phrase refers to a growing set of yield strategies built around Bitcoin that operate off-chain or on other networks, while still using BTC as the underlying asset. Understanding how these systems work requires clarity on Bitcoin onchain constraints, bridging mechanisms, and the evolving BTCFi landscape.
Why Bitcoin Does Not Have Native Staking
Bitcoin does not support native staking at the protocol level, although a small number of external protocols explore ways to lock Bitcoin onchain for securing other networks without changing Bitcoin’s consensus model.
Bitcoin security is enforced through proof-of-work mining, where miners expend computational energy to validate transactions and produce blocks. (Bitcoin Whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf) There is no protocol-level mechanism to lock BTC in exchange for validation rights or yield, unlike Ethereum or other proof-of-stake networks.

This design is intentional. Bitcoin onchain logic is deliberately limited to reduce attack surfaces and governance complexity. While features such as multisignature wallets and timelocks exist, Bitcoin does not support general-purpose smart contracts capable of issuing native staking rewards.
As a result, any yield strategy involving BTC requires an external system. This distinction is critical for institutional risk assessment and custody design.
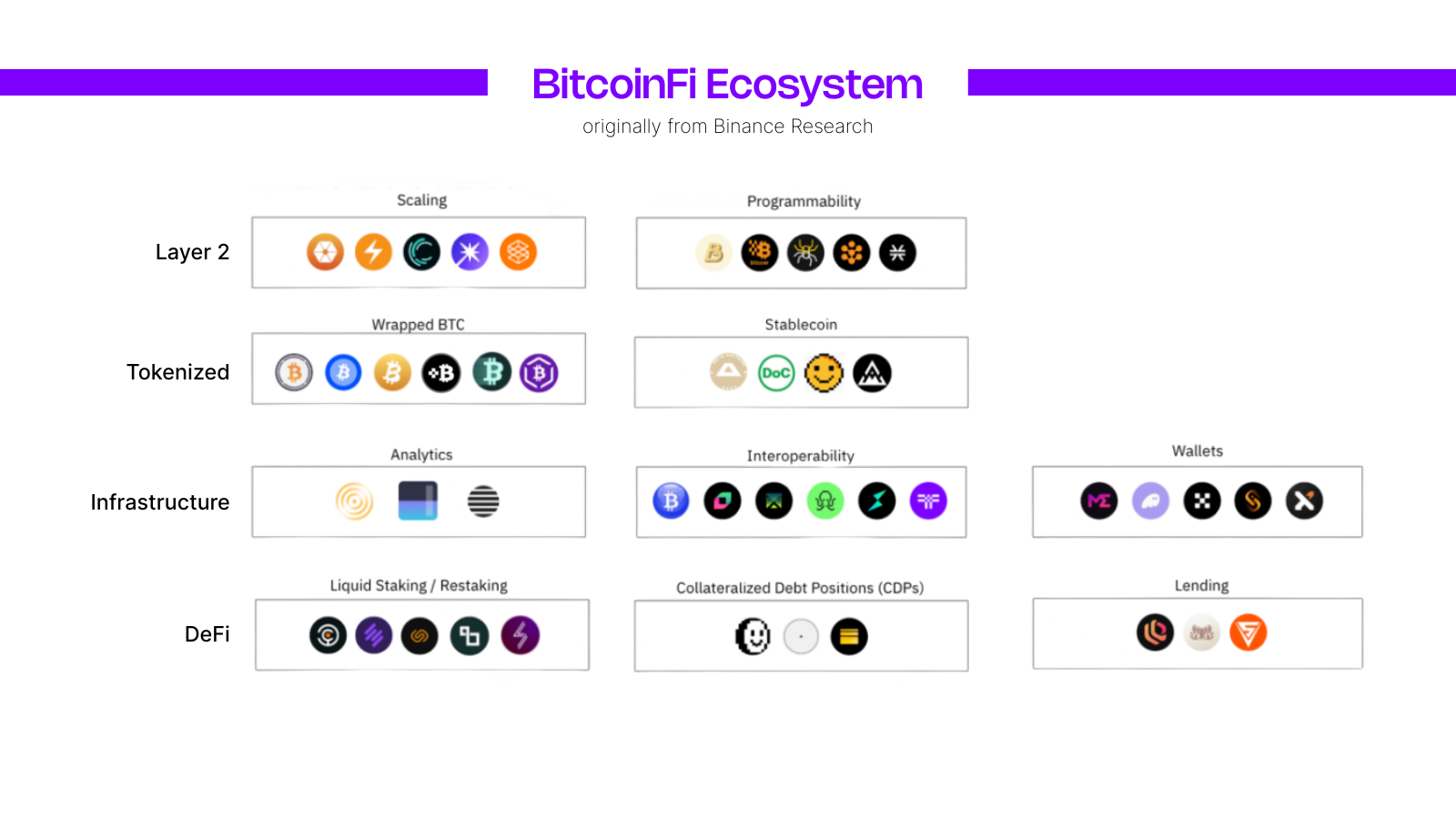
The Emergence of BitcoinFi: Timeline of Events
BTCFi refers to financial infrastructure that enables Bitcoin holders to deploy capital productively without selling BTC. This includes lending markets, derivatives, structured products, and cross-chain applications that extend Bitcoin’s utility beyond simple transfers. (Overview of Bitcoin DeFi concepts https://research.binance.com/en/analysis/bitcoin-defi)
Most BTCFi activity relies on representations of Bitcoin that can operate in smart contract environments. These systems introduce counterparty, smart contract, and bridge risk, but they also enable yield mechanisms that are impossible directly on Bitcoin onchain.
The growth of BTCFi has accelerated as institutions seek BTC-denominated returns rather than yield converted back into fiat or stablecoins.
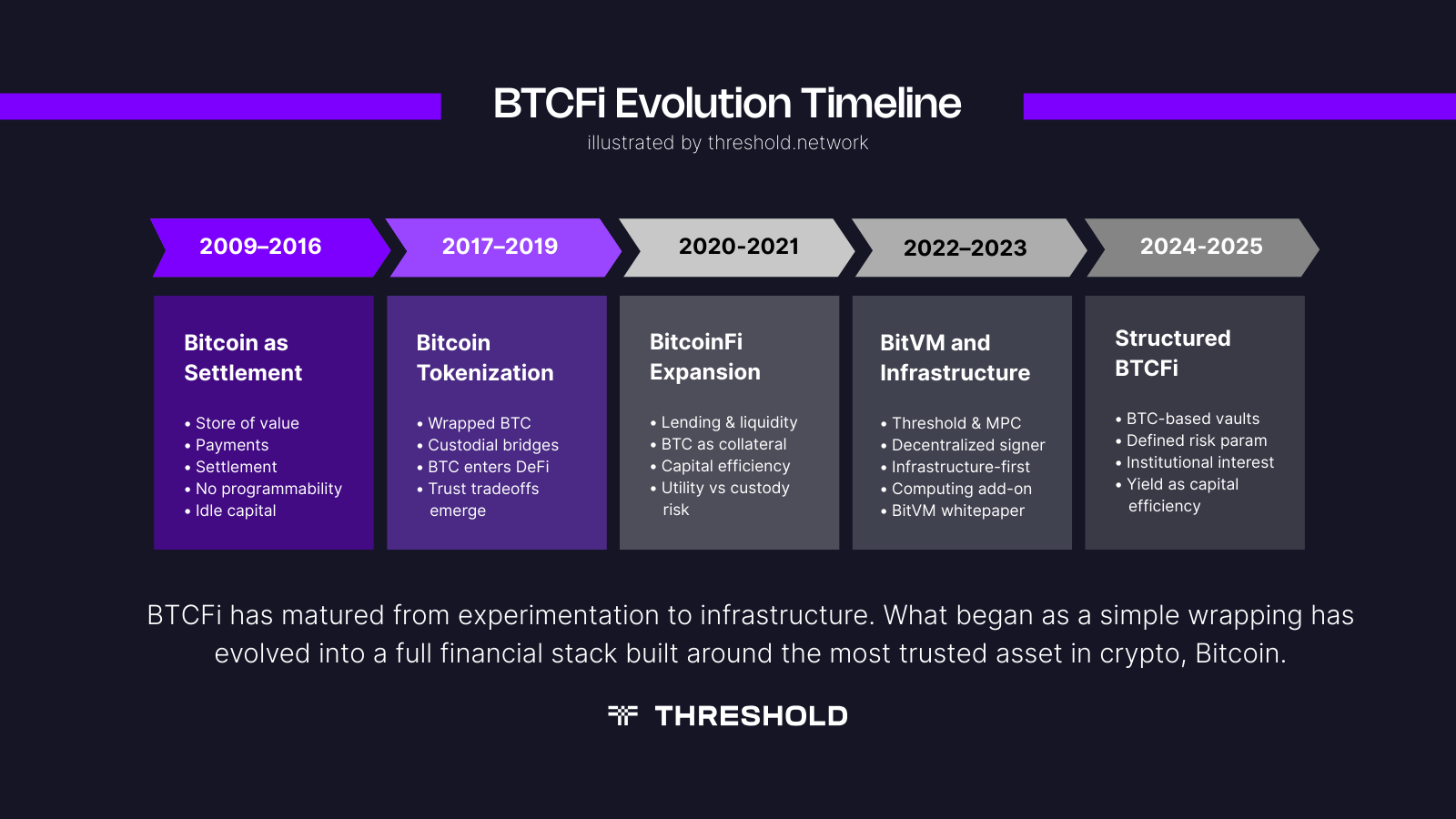
Wrapped Bitcoin and Synthetic BTC
Wrapped Bitcoin is a tokenized representation of BTC on another blockchain. The most common example is WBTC on Ethereum, where BTC is custodied by a centralized entity and minted as an ERC-20 token at a 1:1 ratio. (Reference: WBTC documentation)
These assets enable Bitcoin holders to participate in lending, liquidity provision, and other yield strategies. However, many rely on significant trust assumptions around custodianship and governance.
Wrapped Bitcoin solutions such as WBTC depend on centralized issuers. While they benefit from deep liquidity and broad DeFi integration, some institutions view this model as misaligned with Bitcoin’s principle of trust minimization.
This is where Threshold Network provides a differentiated approach. Through tBTC, Bitcoin can be brought onchain in a trust-minimized manner, preserving Bitcoin’s security assumptions while enabling its use across DeFi.
Bitcoin Bridges and Trust-Minimized Design
A Bitcoin bridge enables BTC to move between Bitcoin and other networks. Bridges vary widely in security architecture, ranging from fully custodial models to threshold-based cryptographic systems.
The core challenge of any Bitcoin bridge is verifying Bitcoin onchain events in an external environment without compromising custody. This is where threshold cryptography and distributed signing become relevant.
Bridges are not neutral infrastructure. Their design directly impacts custody risk, slashing exposure and operational controls.

Threshold Network and tBTC
Threshold Network offers a trust-minimized approach to bridging Bitcoin through tBTC, a decentralized Bitcoin-backed asset. Instead of relying on a single custodian, tBTC uses threshold cryptography to distribute control of BTC across independent node operators.
BTC deposited into tBTC remains fully backed and redeemable, while allowing the asset to be used in smart contract systems. This model reduces single points of failure and aligns more closely with institutional custody requirements.
tBTC is often used as the base layer for Bitcoin yield strategies that aim to minimize trust while enabling programmability. (Threshold Network documentation https://docs.threshold.network)
Bitcoin Staking is a Capital Deployment Strategy
Bitcoin does not offer native staking. Any BTC “staking” product is, in practice, a capital deployment strategy layered on top of Bitcoin.
For allocators, this shifts the evaluation from protocol issuance or validator rewards to:
- How BTC is deployed
- Where yield is sourced
- What risks are introduced relative to holding spot BTC
The core question is no longer “What is the APY?” but “What risks am I underwriting to earn incremental return on BTC?” Recent products show a clear shift away from opaque, discretionary yield and toward:
- Defined leverage limits
- Explicit liquidation parameters
- Automated risk managementTransparent fee structures
This aligns BTC yield more closely with structured finance, making it easier to underwrite within an institutional risk framework.
Allocators should expect fewer “yield promises” and more rule-based strategies with clearly documented mechanics.
The Direction of Bitcoin Yield Markets
Bitcoin yield is moving towards more transparent, modular, and risk-segmented designs. Trust-minimized bridges like tBTC, improved onchain monitoring, and institutional-grade custody integrations are shaping the next phase of BTCFi.
Rather than transforming Bitcoin itself, these systems treat Bitcoin as pristine collateral and build financial layers around it. This preserves Bitcoin’s core properties while expanding its role in global financial markets.
For institutions, the question is no longer whether Bitcoin can generate yield, but under what assumptions, controls, and risk frameworks that yield is acceptable.
You can check out Staking Options for tBTC via https://app.threshold.network/use-tbtc?category=staking
1
0
 Administra todas tus criptomonedas, NFT y DeFi desde un solo lugar
Administra todas tus criptomonedas, NFT y DeFi desde un solo lugarPara comenzar, conecta de forma segura el portafolio que estés utilizando.




