What Is Uniswap and How Does It Work
Uniswap is an open-source decentralized exchange (DEX) initially built on top of Ethereum’s blockchain, that now supports numerous chains.
The protocol, as a decentralized entity, has no listing process, meaning that anyone can list a token on the exchange as long as they provide some liquidity for the traders through a liquidity pool. As a result of this, Uniswap charges no listing fees whatsoever.
When it comes to trading on Uniswap, we can consider it an automated liquidity protocol. This means that the exchange has no order book. Rather, it created its own way of determining buying and selling prices, which we will explain further in the article.
Executive Summary
- Uniswap is an open-source decentralized exchange (DEX) initially built on top of Ethereum’s blockchain, that now supports numerous chains.
- It is an automated liquidity protocol, meaning that the exchange has no order book, but rather a unique way of providing liquidity.
- Anyone can list their token, trade, stake, as well as participate in the governance process of Uniswap.
- Uniswap went through numerous iterations, now being on the third one (Uniswap V3).
- Uniswap is currently the largest AMM DEX, with its UNI token being the 19th largest cryptocurrency by market cap.
Who Are the Founders of Uniswap?
Hayden Adams created and launched the first version of Uniswap in 2018. However, the exchange has gone through a couple of updates, mainly the 2020 Uniswap V2 launch, as well as the 2021 Uniswap V3 launch..
Why Was Uniswap Created?
Uniswap was created as a response to centralized exchanges, which were showing their inefficiencies in the security and decentralization departments. On top of that, other DEX solutions were highly illiquid and not very user-friendly, which created space for Uniswap’s automated liquidity idea.
This gave the crypto sector a decentralized exchange with low trading fees, high levels of decentralization and censorship resistance, as well as great liquidity.
Why Is Uniswap Popular?
Uniswap has popularized the decentralized exchange idea mostly thanks to its easy-to-use and intuitive design, as well as due to users no longer having to worry about insufficient liquidity.
It’s easy to simply connect a crypto wallet, buy or sell your crypto, or deposit your digital assets to a liquidity pool.
What Is Uniswap (UNI) Token?

The UNI token is the backbone of the Uniswap protocol. It is the governance token of the ecosystem. It was distributed to users who provided liquidity to the protocol in its early days, as well as to those who used it frequently. Learn more about “How to Buy Uniswap (UNI)”.
Nowadays, the UNI token allows users to participate in governance decisions regarding the future of the protocol. This includes voting on listing new tokens, or on upgrading the Uniswap exchange.
Although it’s far down from its $43.16 all-time high, UNI is now the 19th largest cryptocurrency by market cap.
How Many Uniswap (UNI) Tokens Are in Circulation?
Uniswap (UNI) has a maximum token supply of 1,000,000,000 UNI. All of the UNI tokens will become available over the course of four years. When it comes to its circulating supply, 75% of the total UNI supply is now in circulation.
After four years after the protocol launch, when all of these tokens have been distributed, Uniswap announced that they will introduce an inflation rate of 2% per year in order to maintain proper network participation.
A total of 60% of the UNI token supply was airdropped to Uniswap community members. The remaining 40% will be distributed to team members, as well as investors and advisors that helped with the project.
What Gives Uniswap (UNI) Tokens Value
Uniswap’s cryptocurrency, UNI, plays a key role in maintaining and operating its network.
Users who hold UNI tokens have the ability to help govern the protocol and vote on proposals that might further Uniswap’s development.
The protocol’s aim is to decentralize decision-making, thus the direction of the protocol is managed by governance votes from UNI token holders rather than by a centralized team or company.
Uniswap delivered on that vision when it distributed 60% of its total supply to its users. Most notably, it did so by sending 400 UNI to every single user on September 1st, 2020. Furthermore, it rewarded the users who had contributed to liquidity pools with some additional tokens.
How Does Uniswap Work?

Now that we have covered what Uniswap is, we are ready to cover its ecosystem’s inner workings.
We can split the Uniswap ecosystem into three main parts:
- Uniswap liquidity pools (liquidity provision)
- Cryptocurrency trading
- Uniswap Governance
Uniswap Liquidity Pools
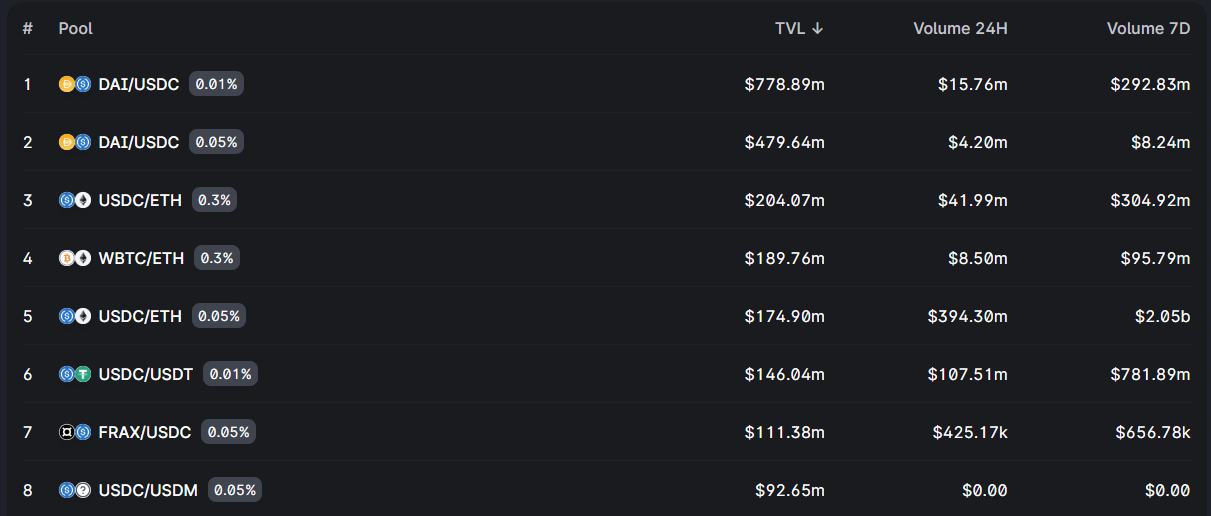
As we mentioned before, Uniswap doesn’t have any order books as centralized exchanges do. Instead, it works with a set of smart contracts called Automated market makers (AMM).
Automated market makers are smart contracts that hold liquidity reserves or liquidity pools that users can trade against. In essence, before any trading between two cryptocurrencies happens, we need to have a liquidity pair. This is achieved by a liquidity provider depositing an equivalent value of two tokens in a pool.
When people buy more than they sell, the equilibrium between the cryptocurrencies in the pool changes, and the price moves accordingly. This increases or decreases the price of a particular crypto in a protocol. Most smaller cryptocurrencies are paired against Ethereum (ETH), or some stablecoin.
Other users can also deposit funds to the liquidity pool, therefore providing liquidity. In return, they get a liquidity pair NFT, which represents their share of the liquidity pool. They receive a portion of transaction fees (Uniswap charges a % fee for each trade) for that liquidity pool that represents their share in the pool.
Cryptocurrency Trading on Uniswap
When it comes to trading cryptocurrencies on Uniswap, we can approach it from the user’s perspective.
Whenever we want to exchange one cryptocurrency for another, we need first connect our web3 wallet, and then find an appropriate liquidity pair for it. Once we have done that, all we need to do is execute the trade, which will cost us 0.3%.
However, we have to pay attention to the depth of the liquidity pool, as well as the size of our order. The larger the order is, the larger the effect on the pool’s liquidity. Likewise, the smaller the liquidity pool depth is, the larger the impact of every order. This can lead to large price fluctuations mid-trade, called slippage.
In order to protect its user from slippage, Uniswap allows its users to select the maximum slippage amount they are willing to accept.
Uniswap Governance

As we have explained above, anyone holding the UNI token can participate in the decision-making process of the Uniswap protocol.
They can do so by voting on different proposals that will determine the future of Uniswap’s development. However, in order to submit proposals to the Uniswap networks, the protocol requires you to own a minimum of 1% of the total UNI supply.
Using Uniswap: Example
Let’s bring the inner workings of the Uniswap protocol closer to you with an example. Let’s say we want to buy USDC with ETH, meaning we need to access the USDC/ETH pool.
We’ll call the USDC portion of the pool “x” and the ETH portion “y”. Uniswap takes the quantity of the two cryptocurrencies in a pool and multiplies them to calculate the total liquidity in the pool. Let’s call this k. According to their whitepaper, the core idea behind Uniswap is that k is constant, meaning that any changes to the x or y will change the price of the cryptocurrency. So, the formula for total liquidity in the pool comes to:
x * y = k
If we want to buy 1,500 USDC tokens with the 1 ETH we have, we can use the USDC/ETH pool. We will pay the 0.3% fee (which gets distributed amongst liquidity providers), and get our 1,500 USDC tokens. However, as a result of our trade, the pool now has 1,500 USDC less and 1 ETH more in the pool. Since the pool has to maintain its total pool liquidity, the only variable that can change is the price of USDC or ETH. This means that, after our trade, USDC is now a little more expensive for the next trader, while ETH is a bit less expensive.
Impermanent Loss on Uniswap
Impermanent loss is one of the risks associated with providing liquidity on Uniswap. When you want to provide liquidity to a liquidity pool, you need to deposit both cryptocurrencies that make up the pool. However, as the price of one cryptocurrency changes, the balance in the pool disrupts as well. As a result of that, it might have been more profitable to just hold the two cryptocurrencies without providing liquidity. The loss caused by this event is called impermanent loss.
Impermanent loss is, as the name says, impermanent until you withdraw your funds. However, liquidity providers must keep it in mind when estimating their profits, as the risk of impermanent loss is always present.
Uniswap V1
Even though it wasn’t the first DEX, Uniswap was certainly the first one to catch the eye of crypto enthusiasts. Before Uniswap, EtherDelta was pretty much the only DEX that captured some traction. However, it was based on the order book model, which suffered from problems such as high costs, poor user experience, and a lack of liquidity.
Uniswap’s V1 was the first decentralized exchange that introduced a non-order book model, which is one of the main reasons it gained traction.
Uniswap v1 supported only ETH/ERC-20 trading pairs, meaning that you could swap only Ether for another ERC-20 token. If you wanted to trade between two ERC-20 tokens, you had to trade your first token for ETH, and then that ETH back for the second ERC-20 token.
Uniswap V2 vs. Uniswap V3
We have mentioned that Uniswap has gone through three phases after it was first released. Uniswap V2 has brought massive improvements to the exchange, introducing ERC-20/ERC-20 pairs, meaning you could easily trade your non-Ethereum altcoins for one another. Additionally, Uniswap V2 has brought a decentralized on-chain price feed, provided by Oracles. This is also when Uniswap introduced a protocol fee, which took 0.05% of the 0.3% trading fee to fund future development.
The next and current iteration of Uniswap is its third version. Uniswap V3 has brought numerous improvements to the protocol, including:
- Capital efficiency
- Flexible fees
- Uniswap LP NFT tokens
- Advanced oracles
- License changes
Capital Efficiency
One of the biggest improvements coming with Uniswap V3 relates to capital efficiency.
Most AMM smart contracts have proven themselves as very capital inefficient. This is because funds deposited to them were often just sitting idle. This meant that Uniswap often found itself having massive amounts of funds sitting in its pools, while daily volumes were several times lower.
Uniswap V3 addressed this issue by allowing liquidity providers custom price ranges for which they want to provide liquidity for. This means that pools need less liquidity to maintain certain price ranges.
This improvement has brought Uniswap closer to order book exchanges, as liquidity providers could choose the price range they want to be in – which looks a lot like a limit order on traditional centralized exchanges. However, the protocol still maintained the identity that caused it to gain such popularity.
Additionally, this meant that liquidity providers that used a “set it and forget it” strategy would earn far less than those that optimized their price ranges.
Flexible Fees
Uniswap v1 had introduced a flat 0.30% fee structure, of which 100% goes to the liquidity provers. The second version of Uniswap (v2) then introduced a 0.05% protocol fee which could be turned on/off depending on the will of the users through governance.
Uniswap v3 has brought community-governed flexibility through multiple fee tiers:
- 0.05% – expected for stablecoin pools
- 0.30% – for standard pools like ETH/USDC
- 1.00% – for exotic pairs
The Uniswap team then introduced even more flexibility by allowing users to vote on adding additional fee tiers.
Uniswap LP NFT tokens
As liquidity providers are now able to choose their custom price ranges, the prior model of liquidity pair tokens wasn’t going to work. This is why Uniswap V3 has introduced non-fungible tokens to represent its custom range liquidity providers.
Advanced Oracles
One important back-end change was the way Uniswap handles oracles. Without going into too much detail, this improvement made it easier and cheaper to create advanced oracles, thus reducing the gas cost for keeping the oracles running by up to 50%.
License Changes
One somewhat controversial change introduced by Uniswap V3 was the change in the smart contract license. Due to its open-source nature, Uniswap V2’s rising popularity has brought numerous Uniswap clones that just copied the code and changed branding.
Uniswap’s V3 has introduced a license that would prevent copycats from stealing the code, thus protecting the protocol from being copied, but also hurting the open-source philosophy of blockchain technology.
Uniswap on Layer 2
With transaction fees on Ethereum going through the roof in 2021, the usage of Uniswap became too expensive for most users.
As a response, Uniswap branched out to a layer 2 calling solution called Optimistic rollup. As layer 2 solutions benefit from the main layer’s security, Uniswap was still as secure as before, while providing users with a cheaper solution for their day-to-day swaps.
Additionally, Uniswap has launched its protocol on the Polygon blockchain in December 2021.
Nowadays, Uniswap supports numerous blockchains, such as Ethereum, Polygon, Optimism, Arbitrum, Celo, with more certainly to come in the future.
How Does Uniswap Make Money?
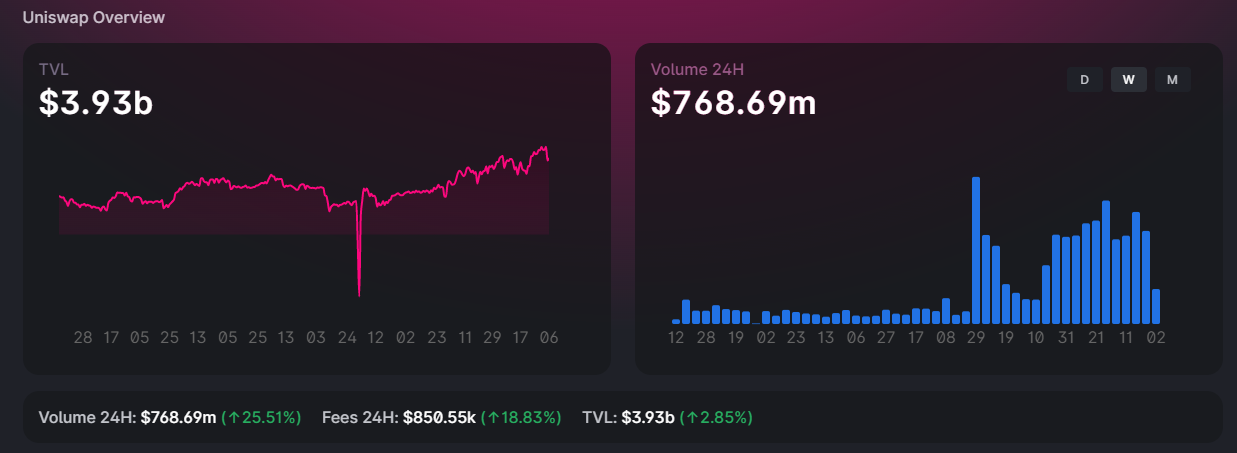
Uniswap essentially makes money in two separate ways: protocol fees and UNI token appreciation.
As we have mentioned, Uniswap users have the option to turn on protocol fees, which take a portion of trading fees and put it towards future protocol development. While it may sound insignificant, Uniswap managed to generate over $1 billion in revenue in 2021 alone. However, most of the revenue went towards liquidity providers, but the company still managed to earn $40 million.
The other way Uniswap, or rather its founders and employees, make money, is through the appreciation of the UNI token. Uniswap employees hold 20% of the total UNI token supply. This means that any appreciation of the token means huge profits for the Uniswap team. With the current market capitalization of $4.75 billion, Uniswap employees hold well over $1 billion in UNI tokens.
Is Uniswap Safe?
Uniswap has proven itself as a safe exchange, as it operates as a decentralized exchange and liquidity pool. Due to its decentralization and the fact that is built on Ethereum, it essentially borrows the security of the Ethereum blockchain.
Unlike centralized exchanges, Uniswap has no custody over users’ funds, as well as no central server to hack or gain access to users’ funds.
When it comes to providing liquidity, the funds are deposited into a highly-secured and audited smart contract. Any funds you deposit could only be removed by the same crypto wallet.
Uniswap’s smart contracts have been thoroughly tested and audited by large auditing firms. Additionally, Uniswap is offering a bug bounty program, which incentivizes anyone that finds bugs to present them to the team rather than abuse them, as they will get rewarded financially for doing so.
In essence, as long as you keep your personal wallet safe, Uniswap exchange is safe to use.
Bottom Line
Uniswap is one of the largest AMM decentralized exchanges on the Ethereum blockchain, as well as the crypto sector. The exchange currently occupies 43.7% of the market.
Its intuitive and user-friendly design, revolutionary features, as well as great reward programs, has made Uniswap what it is today. To top that off, Uniswap strives towards decentralization and censorship resistance, which certainly comes as a bonus. Its intuitive design (both in terms of smart contracts and UI) made it a respectable name in the industry. This has, in turn, made it the DEX protocol most others copied.
While majorly affected by the skyrocketing Ethereum fees in 2021, the protocol is hoping to benefit from Ethereum’s scalability solutions.