What Is DeFi [The Ultimate Guide 2023]
Reviewed By: Adrian Zmudzinski
Short on time? Listen instead.
Decentralized Finance DeFi is one of the biggest trends in the blockchain industry, and many believe it will overtake the traditional finance world. DeFi uses DApps and distributed ledger technology (DLT) to allow for permissionless financial operations to be conducted within a peer-to-peer network.
Experts believe that the massive adoption of DeFi will be exponential thanks to DeFi products like efficient stablecoin trading, decentralized lending or Yield Farming, DEX (Decentralized exchanges), DeFi insurance, liquidity mining, etc.
Read on for CoinStats ultimate guide to learn everything you need to know about the DeFi space, popular DeFi protocols, DApps, and download our CoinStats Wallet that lets you coordinate all your DeFi activity from one place.
Let’s dive in!
What Is DeFi
DeFi is an umbrella term for peer-to-peer financial services and one of the most important innovations of blockchain technology, revolutionizing the global economy. It operates according to a protocol that runs on a blockchain-powered decentralized network.
DeFi redefines traditional financial services such as lending, trading, investment, payment, insurance, and others by disrupting the role of intermediaries.
Regular financial services are centralized in nature and controlled by government agencies, financial institutions, and other intermediaries in contrast to DeFi, which is permissionless, decentralized, and borderless.
To better understand Decentralized finance, let’s look into how centralized finance works.
What Is Centralized Finance
Under a regular or centralized financial system, you hold your money in a bank account owned by financial institutions that act as a centralized authority. Many third-party intermediaries levy a fee every time you spend your money from your account, i.e., while using credit cards. Banks also charge a specific fee for holding your money and making a financial transaction.
Additionally, it takes weeks or even months to secure a loan under a centralized financial system. Moreover, the loan is only secured after approval for your credit score and history.
In a centralized financial system, all financial transactions are monitored and governed by a centralized authority, making them more complicated, lengthy, and expensive.
What Separates Decentralized Finance From Centralized Finance
In decentralized finance, the need for financial intermediaries and third-party institutions is eliminated by using distributed ledger technology (DLT) or blockchain. The intermediaries become replaced by smart contracts, thereby enabling almost instantaneous peer-to-peer transactions and payments.
The instantaneous and low-cost DeFi transactions also play a significant role in scalability. Moreover, DeFi provides access to financial systems to anyone with an internet connection. The money is stored in decentralized wallets such as the CoinStats Wallet and can be used just like regular money.
How Does DeFi Work
DeFi operates on blockchain technology that acts as a distributed ledger and stores all the data about the transactions over the blockchain. The system eliminates the control of institutions on money, financial products, and financial services. DeFi is a trustless network where users are given complete control over their assets and investments; they don’t need third-party authentications.
DApps or decentralized applications handle all the transactions on the blockchain. The verification for the transactions stored on the blockchain is made by other users’ connections over the blockchain. This verification process uses the computing power of the users’ devices on a Proof-of-Work blockchain. In the case of a Proof-of-Stake blockchain, the transactions are verified using the tokens staked by the users over the blockchain.
Decentralized Financial Applications and Services
DeFi applications, DeFi transactions, etc., are conducted within a peer-to-peer network, which means that the transactions occur between two parties directly without the need for any intermediary. Transactions are governed by smart contracts, which are one of the most valuable features in DeFi, upholding transparency and visibility on the blockchain. A smart contract works by creating an automatic and self-executing agreement whereby each party inputs predetermined conditions that must be completed for the contract to be executed without a central authority or third party.
DeFi protocols aim to provide equal access to all financial services worldwide. Consider how you obtain a loan in traditional finance. You’d have to request it from your financial institution or another middleman, and you’ll have to pay tax and processing fees to use the lender’s facilities if you’re authorized. Defi users are free from these restrictions, as thanks to blockchain technology, no one controls the DeFi platform. DeFi lending platforms employ smart contracts to eliminate the need for middlemen. So if an individual applies for a loan on a DeFi platform after providing personal information and undergoing verification, the DeFi applications connect them directly to another individual willing to give out the loan. These loans are given out in digital assets such as stablecoins or other digital assets at specific interest rates agreed between the loanee and lender.
A DeFi application is essential as:
- It eliminates the fees charged by financial companies for utilizing their services.
- It helps you save your cash in a secure virtual wallet instead of keeping it in banks.
- Anyone with an internet connection can use it without needing permission.
- It allows you to carry out transactions faster.
Some of the most popular types of DeFi applications include:
- Staking platforms
- Liquidity mining platforms
- Decentralized exchanges (DEX)
- Decentralized lending protocols and apps
- Non-custodial wallets.
Common Uses of DeFi
The ease with which we conduct transactions using Decentralized finance (DeFi) apps has made them popular. There has been a massive increase in DeFi applications and financial services. Some of these most common use cases for DeFi are:
Decentralized Exchanges
Cryptocurrency exchanges are digital marketplaces where individuals can trade in cryptocurrencies NFTs and even stake their tokens to earn interest on them. Cryptocurrency exchanges can be centralized and decentralized. A centralized cryptocurrency exchange is like a traditional exchange, but for trading in digital assets. They are governed by a centralized system and charge their users specific fees for using their services. Some of the most famous centralized crypto exchanges are Binance, Kucoin, Huobi, etc.
On the other hand, a decentralized exchange (DEX) is not governed by any central authority; instead, it operates over blockchain and charges no fee except for the gas fee applicable on a particular blockchain, i.e., on the Ethereum blockchain. The most popular decentralized exchanges are Sushiswap, UniSwap, etc. These exchanges use smart contracts to allow people to trade in crypto assets without the need for a regulatory authority. They deploy an automated market maker to remove any intermediaries and give complete control over the funds to users. Although this brings a lot of freedom and power to the user, the risk mitigation is also high. For example, if a user sends money to the wrong address or loses the keys to their wallets, recovering the lost funds won’t be possible. This has been one of the reasons for most beginners to prioritize trading on centralized exchanges. Despite the risks involved, decentralized exchanges have been growing over recent years, and almost every major blockchain in the world has its own DEX.
Sending Money
DeFi projects make it possible to send money across the globe almost instantaneously by using smart contracts. Similar transactions in traditional finance can take from days to weeks to process. On top of that, there will always be a fee associated while carrying out these transactions. This is where DeFi applications make sure these transactions occur in real-time and are instantaneous in nature except for the time taken for the transaction to go through on the blockchain. Many DeFi apps make sending money easy and seamless without the need for an intermediary. Moreover, transaction costs with DeFi apps are significantly lower than for traditional services thanks to the efficiency of blockchain, the automation of smart contracts, and their immutability.
Stablecoins
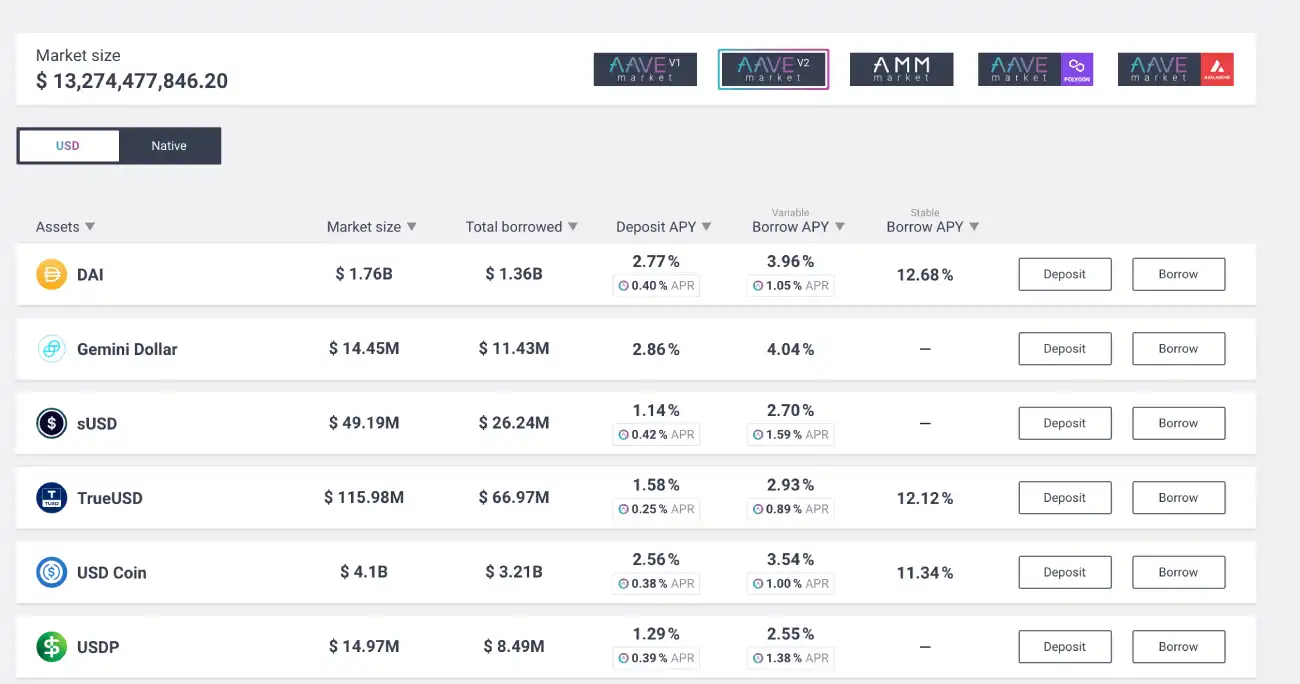
Stablecoins are digital currencies backed by assets such as fiat currency, other cryptocurrencies, or gold. Most commonly, stablecoins are pegged against the U.S. dollar, and their price never goes a few cents over or below the price of the U.S. dollar. The most commonly used stablecoins are USD Tether(USDT), USD Coin(USDC), DAI, etc. While USDT and USDC are centralized stablecoins issued by a centralized authority, DAI is a stablecoin, pegged against the U.S. dollar and issued by MakerDAO, a DeFi platform.
DeFi Borrowing
DeFi allows users to borrow money in the form of a digital asset. There are two types of borrowing – peer-to-peer borrowing and borrowing from liquidity pools. In peer-to-peer borrowing, individuals can borrow from one another directly using smart contracts, whereas, in a liquidity pool-based borrowing, lenders provide liquidity in the form of cryptocurrency assets to the lending pools. While in traditional borrowing, there is a need for credit checks and other formalities, in the DeFi space, borrowing occurs without any checks by deploying a smart contract. The borrower’s collateral is automatically transferred to the lender if the borrower fails to repay on time.
Flash Loans
Flash loans are the latest and more technical aspects of the DeFi ecosystem. They are technically collateral-free loans that are instantaneous in nature. Getting a flash loan requires technical knowledge of how coding, blockchain, and smart contracts function. In flash loans, the lending, borrowing, and returning of the loan all occur simultaneously. To understand how it works, let’s say you borrow an asset from an exchange or lender for $1 and then sell it on another exchange for $1.5. In the same transaction, you can return the amount you borrowed and pocket the price difference on different exchanges as your profit. Many experienced cryptocurrency traders use this method to make money. If the transaction fails to go through for some reason, the money is returned to the lender’s account automatically. All these processes occur simultaneously, making a flash loan instantaneous in nature.
Yield Farming
Yield farming or liquidity mining is one of the most popular use cases of DeFi and forms the core of decentralized lending. It’s based on the principle of decentralized lending, whereby lenders act as liquidity providers to the liquidity pools, and borrowers borrow tokens from the same pool. In return, the liquidity providers earn interest and fees, which are distributed among them in accordance with the liquidity they have provided. Many cryptocurrency exchanges also provide the option of yield farming, and the exchange commission or fee associated with it is distributed among the liquidity providers.
Prediction Markets
Prediction markets are other examples of DeFi uses that involve betting on future events like the outcome of a sporting event, races, election results, etc. Prediction markets are one of the most emerging and lucrative opportunities amongst the DeFi products.
Non Fungible Tokens
We distinguish between fungible and Non-fungible tokens (NFTs). A fungible token can be exchanged for another, while NFTs aren’t interchangeable and are built over the blockchain. DeFi is what has made NFTs possible. In recent years, NFTs have taken the world by storm and impacted the global economy, with several mainstream organizations and companies endorsing them and making huge profits. NFTs were built on the Ethereum blockchain but are now available across a whole spectrum of blockchains, including the Binance smart chain.
NFTs are among DeFi applications that have found the most use cases and made millions for artists. One of the biggest NFT platforms is OpenSea, with a trading volume of more than $3.5billion USD, and a large number of such platforms are coming up, i.e., Rarible, etc. By the way, you can also check out CoinStats NFT collections on Opensea
Margin Trade
One of the more profitable but riskier aspects of DeFi is margin trading. In margin trading, a trader borrows capital from a broker and uses it to trade in the open market with leverage. Margin trade requires you to deposit particular capital to be eligible for trading. The deposited capital acts as collateral and a guarantee in the market if you cannot repay the funds you borrowed. Like other trades, margin trades also have a fee collected from the trader.
Conclusion
DeFi has come a long way in a short span of time and has proven to be an avenue that allows its users to capitalize on it. DeFi services such as lending, yield farming, flash loans, margin trading, and especially NFTs have revolutionized the global economy and brought financial freedom to everyone worldwide. DeFi is also the big reason behind the crypto market attracting more and more users every day and the possible mass adoption of cryptocurrencies and blockchain in the future.
While currently, Ethereum is the backbone for DeFi, other blockchains such as Solana, BSC, etc., are coming up with their own decentralized products and services that provide multiple new opportunities to users, and DeFi solutions, based on the Bitcoin blockchain, are also in progress.
Additionally, when Ethereum 2.0 comes out, the gas prices on Ethereum would go down substantially, leading to the large-scale adoption of DeFi.





